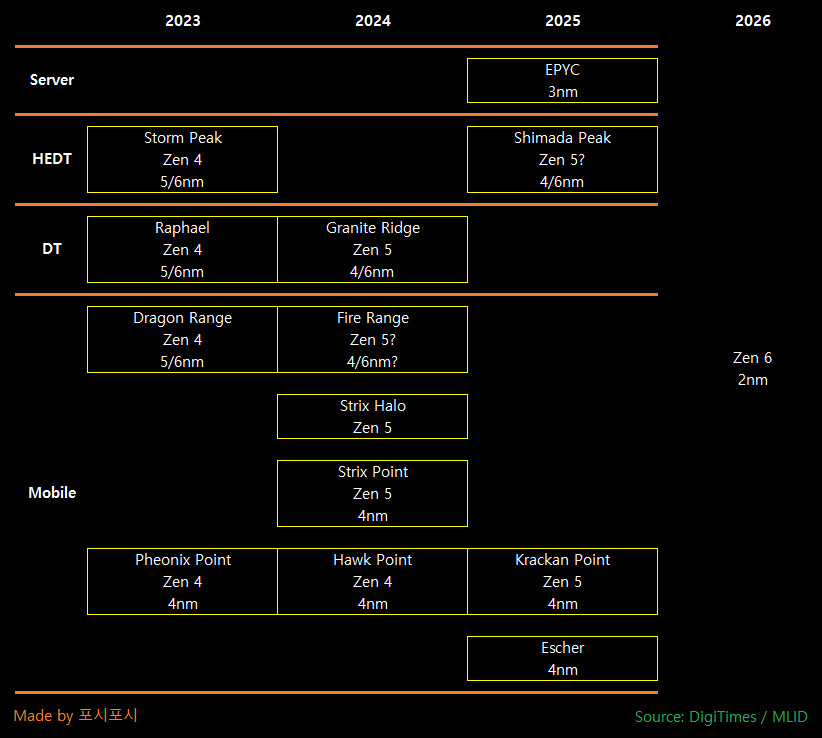
According to insider sources, TSMC's customers are expected to delay the use of the foundry's 3 nm process node until 2024 or later due to a slowdown in the PC hardware market. AMD is reportedly planning to stick with 4 nm and 6 nm nodes for many of its future CPU lineups, with the next generation Zen 5-based family set to launch in 2024. AMD's roadmap, based on DigiTime's findings, suggests that the company will offer a range of mainstream desktop (Granite Ridge) and laptop/mobile CPUs (Fire Range) in 2024, but no high-end desktop (HEDT) options are marked for release that year.
Instead, AMD is said to be planning to release Zen 5-based Ryzen Threadripper processors in the following year, with the codename for the Ryzen Threadripper 8000-series reportedly being "Shimada Peak." Industry experts believe that these HEDT CPUs will eventually succeed the Threadripper "Storm Peak" 7000 family, which is due for launch later in 2023. To avoid costly decisions, AMD is likely to use a shared socket design, as their sTRX4/SP3r3 socket only survived for one generation.